Table of contents

Tabnine and Sourcegraph Cody are AI code assistants. Both products offer AI-powered chat and code completions to accelerate the software development life cycle and support common use cases such as planning (i.e., asking general coding questions or better understanding code in an existing project), code generation, explaining code, creating tests, fixing code, creating documentation, and maintaining code.
However, Tabnine offers significant advantages over Sourcegraph Cody. Unlike Sourcegraph Cody, Tabnine gives you the utmost control over its AI code assistant by allowing you to personalize the AI to your systems and set the privacy and protection trade-offs that fit your security and compliance policies.
This blog post goes through each of the differences between these products in detail, demonstrating why we believe that Tabnine is the ideal choice for enterprises and individual developers.
Even though generative AI for software development has become mainstream in the past few years, there’s still a lot of skepticism around code assistants. How does the AI code assistant handle my data? What data set is the underlying model trained on? Will my code be used to train the model? This skepticism has prevented companies from fully embracing AI for their engineering teams. In this section, we’ll cover how Tabnine and Sourcegraph Cody address data privacy issues.
Data retention policies
Cody does not have its own proprietary models and relies solely on third-party LLMs (e.g., models from Anthropic and Open AI) to generate responses to user prompts, both for its chat and code autocomplete. Due to this inherent limitation, Cody sends your LLM prompts (a combination of your prompt and relevant code snippets from your codebase) to these third-party LLM providers. Additionally, if you enable Cody to generate embeddings for your repository to get personalized results, Cody shares a copy of the entire content in your repository with the third-party LLM provider.
Even on the Cody Enterprise tier, Sourcegraph retains user Prompts (your submissions to Cody, such as a query or request) and responses (outputs returned to you by Cody) for an unspecified duration.
Cody doesn’t train on your company’s data if you’re on their Enterprise tier. However, the data for Pro tier users can be used for training purposes.
Tabnine takes a completely different approach and offers a zero data retention policy. When using Tabnine’s proprietary models, we don’t store customer code, don’t share customer code or usage data with third parties, and don’t use customer code to train our models.
The space for generative AI for software development is evolving swiftly with new, powerful models getting introduced in the market at a rapid pace. We want to enable users to take advantage of all the innovations that come with newer models and so similar to Cody, we too offer models from third-party providers. Users can choose from two custom-built, fully private models from Tabnine; Open AI’s GPT-4o, GPT-4.0 Turbo, and GPT-3.5 Turbo; Anthropic’s Claude 3 Sonnet model; Codestral, Mistral’s first-ever code model; and Cohere’s Command R model. We’ll soon introduce support for more models in the near future.
This flexibility enables users to pick the right model based on their use case or project. For projects where data privacy and legal risks are less important, you can use a model optimized for performance over compliance. As you switch to working on projects that have stricter requirements for privacy and protection, you can change to a model like Tabnine Protected that’s built for that purpose. Enterprises have complete control when selecting models that power Tabnine Chat. Tabnine admins can choose any specific models from the list of available LLMs and make them available to their teams. They can also connect Tabnine to an LLM endpoint inside their corporate network if needed.
Cody is offered as a SaaS product and requires an active internet connection to facilitate the data transmission between IDE and the third-party LLM providers. Due to its reliance on third-party LLMs, there are no plans to provide a completely self-hostable version of Cody, as this option is cost-prohibitive.
This is often a deal breaker for privacy-conscious enterprises, especially in highly regulated environments such as financial services, healthcare, defense, semiconductor, and automotive, as these companies need an air-gapped deployment.
Tabnine offers its customers numerous deployment options. Customers can consume Tabnine as a secure SaaS offering (in a multitenant environment or a single-tenant environment) or do a fully private installation (on-premises or on VPC) to ensure that their code stays within the boundaries of their corporate network and isn’t shared with any external party.
The third-party models used by Cody are trained using a diverse range of publicly available data, which may include copyrighted code. It’s possible for Cody to return code suggestions that match publicly available copyrighted code. If a code suggestion matches proprietary code, there’s a risk that using that suggestion could trigger claims of copyright infringement. To mitigate this legal risk, Sourcegraph offers indemnification to enterprise customers. Another approach used by Cody to minimize the legal risk is using the Guardrails feature (currently in Beta) that checks for code suggestions and informs the user if the suggestions match any proprietary code. However, the Guardrails feature doesn’t work for suggestions that contain fewer than 10 lines of code.
Tabnine eliminates concerns around IP infringement from the get-go. We’ve trained our proprietary models (Tabnine Protected for Chat, and the universal model for code completion) exclusively on permissively licensed code. This ensures that Tabnine’s recommendations never match any proprietary code and removes any concerns around legal risks associated with accepting the code suggestions. Unlike Cody, we’re transparent about the data used to train our proprietary model and share it with customers under NDA. Additionally, we offer an IP indemnification to Enterprise users for peace of mind.
In AI, context is everything. To increase the effectiveness of AI code assistants, it’s imperative to provide contextual awareness to the LLMs so that they can understand the subtle nuances that make a developer and organization unique.
Cody gains context by leveraging the locally available information in the developer’s IDE, and it can also use RAG to gain context for the information that resides in the organization’s codebases. Model fine-tuning is not available.
Tabnine leverages locally available data in the developer’s IDE to provide more accurate and relevant results. This includes runtime errors, imported libraries, other open files, current file, compile/syntax errors, noncode sources of information, current selected code, connected repositories, conversation history, Git history, project metadata, and other project files.
Additionally, users can connect Tabnine to their organization code repos (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket) to gain global context. Tabnine also offers model customization. You can fine-tune our proprietary model using your own code to create a custom model. Model customization is extremely valuable when you have code in a bespoke programming language or a language that is underrepresented in the training data set, such as System Verilog.
Cody is a relatively new product (the first version was released in Dec 2023). This is reflected in lack of support for popular IDEs and significantly low user adoption.
Tabnine is the originator of the AI code assistant category, having introduced our first AI-based code completion tool for Java in the IDE in June 2018. Tabnine is now the leading AI code assistant on the market with one million monthly active users. This enables us to gather feedback from a vast number of users and make continuous improvements and refinements to the product.
IDE support
Tabnine offers much more robust coverage for IDEs compared to Sourcegaph Cody.

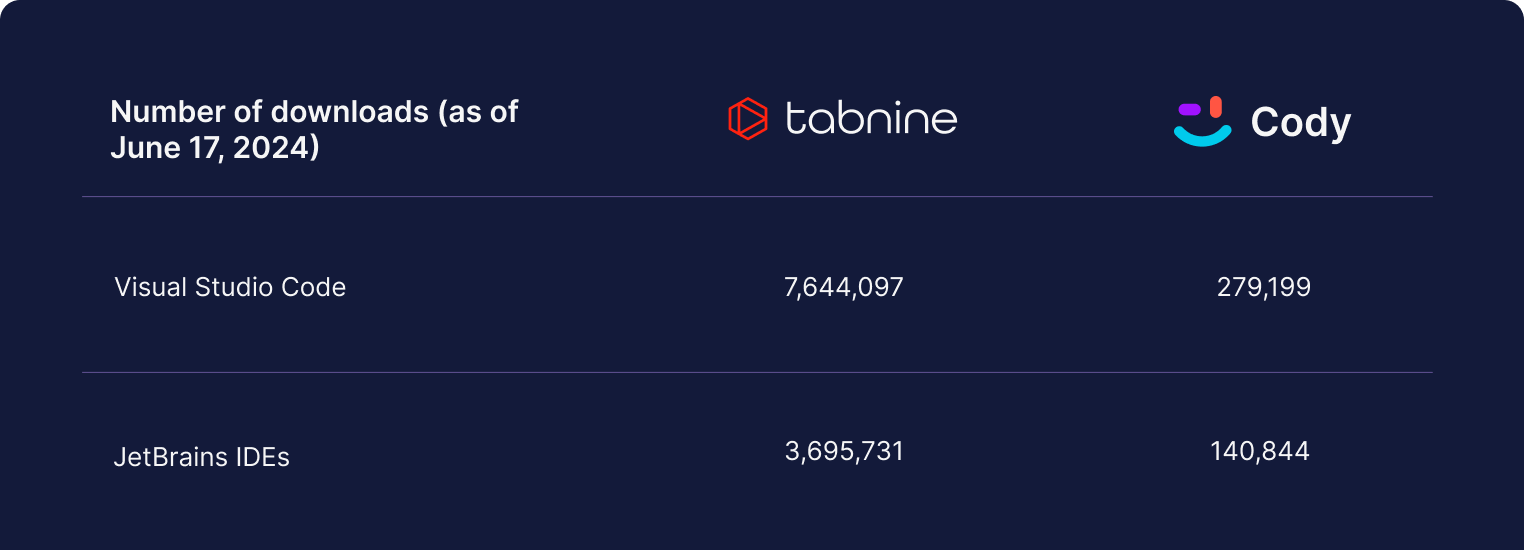
The table below summarizes the differences between Tabnine and Sourcegraph Cody. Both products support common use cases such as code generation, creating documentation, generating tests, and more. However, if you need an AI code assistant that gives you complete control over data privacy, deployment options, personalization, protection from IP infringement issues, and wider IDE coverage, then you should consider Tabnine.

Tabnine is honored to be recognized in Gartner® Critical Capabilities for AI code assistants, which focused “on 14 critical capabilities that align with the five most common Use Cases in AI-augmented development.” Gartner® evaluated 12 vendors, and here’s how Tabnine ranked.
Tabnine is ranked first for:
Tabnine is ranked second for:
Omdia recognized Tabnine in Omdia’s Market Radar for AI-Assisted Software Development.
Tabnine’s position as a leader in this space was recently reinforced as we were featured as a luminary in Everest Group’s Innovation Watch Assessment for Generative AI Applications in Software Development. Everest Group — a world-renowned research firm that provides strategic insights on IT, business processes, and engineering services — assessed 14 leading providers of generative AI solutions for software development for this report. The assessment framework evaluated each provider on four criteria (Scale, Level of maturity, Partnerships, and Investments) and segmented them into four categories (Luminaries, Fast Followers, Influencers, and Seekers). Tabnine performed exceptionally well in the entire assessment framework and is recognized as a Luminary.

Check out our Docs or contact us to schedule a demo with a product expert. If you want to try it out for yourself today, sign up here to try it free for 90 days.